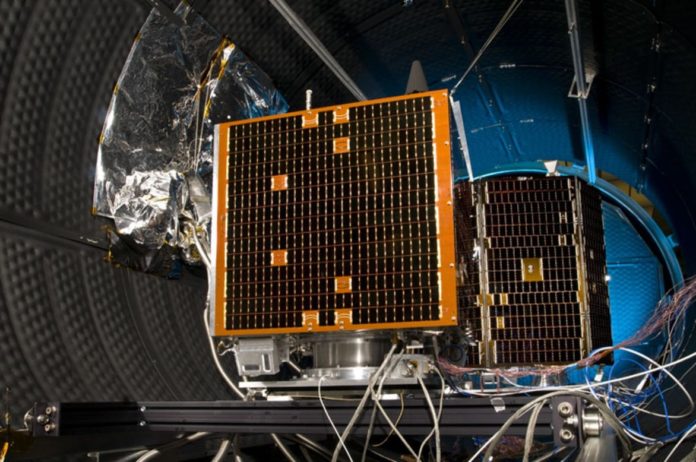
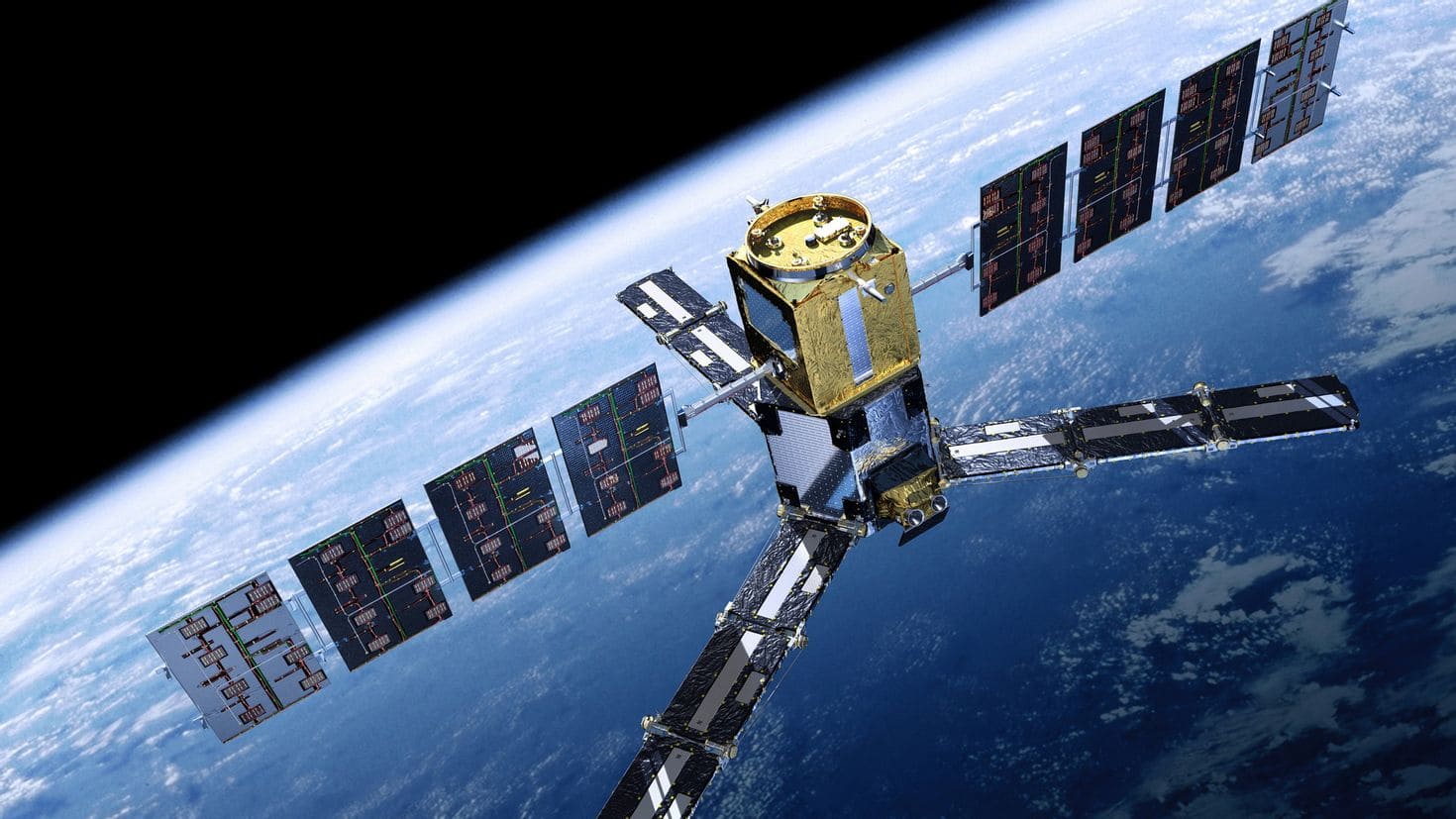
The past five years have been transformative for Africa’s space industry, with significant strides in satellite technology, international collaborations, and policy developments. These advancements have bolstered the continent’s capabilities in areas such as communication, Earth observation, and scientific research, setting a strong foundation for future growth.
Africa’s space industry has experienced remarkable growth and innovation over the last five years. The continent has seen an increase in satellite launches, the establishment of space agencies, and strengthened international partnerships. These landmark developments not only enhance technological capabilities but also contribute to socio-economic growth and environmental monitoring across the continent.
Rise of National Space Agencies
Ethiopian Space Science Society (ESSS) and Ethiopian Space Science Society (ESSS). Ethiopia has made notable progress in its space endeavors with the Ethiopian Space Science Society (ESSS) playing a pivotal role. Established to promote space science and technology, ESSS has been instrumental in driving educational initiatives and scientific research.
South African National Space Agency (SANSA). South Africa continues to lead in the African space sector with the South African National Space Agency (SANSA). Over the past five years, SANSA has focused on developing satellite technology, space weather monitoring, and fostering international collaborations.
Nigeria’s National Space Research and Development Agency (NASRDA). Nigeria’s NASRDA has been at the forefront of space technology development in West Africa. Recent initiatives include the launch of new satellites and advancements in space-based research and applications.
Key Satellite Launches
Ethiopia’s ETRSS-1 Satellite. Launched in December 2019, Ethiopia’s ETRSS-1 (Ethiopian Remote Sensing Satellite-1) marked a significant milestone for the country. The satellite, developed with Chinese collaboration, aims to enhance Ethiopia’s capabilities in weather forecasting, agricultural monitoring, and environmental protection.
Egypt’s TIBA-1 Communications Satellite. In November 2019, Egypt successfully launched TIBA-1, its first communications satellite. TIBA-1 aims to provide high-speed internet and communication services across Egypt and other parts of North Africa, addressing connectivity challenges and supporting socio-economic development.

South Africa’s ZACube-2 Satellite. Launched in December 2018, ZACube-2 is South Africa’s most advanced nanosatellite. It plays a crucial role in maritime domain awareness, offering valuable data for ship tracking and environmental monitoring.

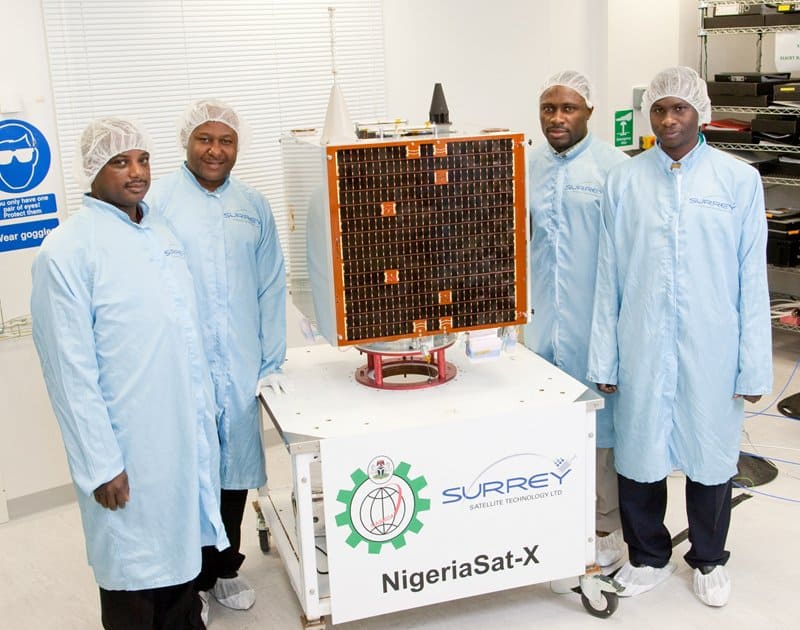
Nigeria’s Sat-2 and Sat-X. Nigeria has made significant strides with the launch of its Sat-2 and Sat-X satellites. These satellites enhance Nigeria’s capabilities in Earth observation, disaster management, and resource monitoring.

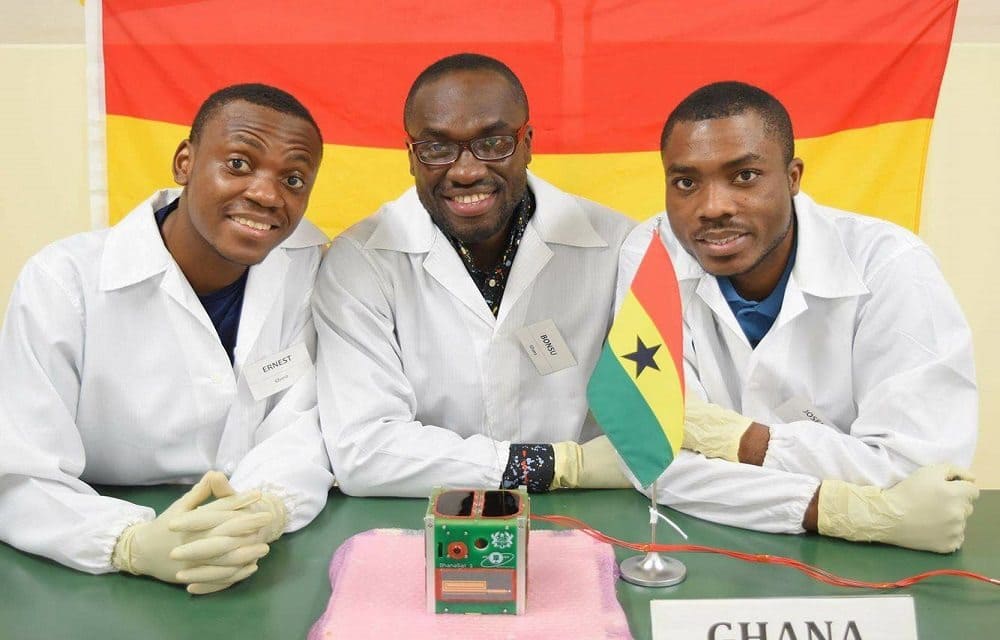
Ghana’s GhanaSat-1. In July 2017, Ghana entered the space age with the launch of GhanaSat-1, its first satellite. Developed by students from All Nations University College in Ghana, the satellite is used for Earth observation and scientific experiments, showcasing the potential of academic institutions in advancing space technology.

Advancements in Earth Observation and Environmental Monitoring
Development of Regional Space Programs. Regional space programs have gained momentum in Africa, promoting collaboration among nations. The African Resource Management Constellation (ARMC), for example, involves several African countries working together to develop and share satellite data for resource management and environmental monitoring.
Remote Sensing and Climate Monitoring. African countries are increasingly leveraging remote sensing technology for climate monitoring and agricultural management. These advancements help in predicting weather patterns, assessing crop health, and managing natural resources more effectively.
Socio-Economic Benefits of Space Technology
Improving Connectivity and Communication. Satellite technology has significantly improved connectivity in remote and underserved regions of Africa. High-speed internet and reliable communication services facilitate education, healthcare, and economic activities, contributing to overall socio-economic development.
Enhancing Disaster Management. Space-based technologies play a crucial role in disaster management and response. Satellites provide real-time data for monitoring natural disasters such as floods, droughts, and wildfires, enabling timely and effective intervention.
Supporting Agricultural Development. Satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies are transforming agriculture in Africa. These technologies provide farmers with critical information on soil health, crop conditions, and weather forecasts, leading to better crop management and increased productivity.
International Collaborations and Partnerships
African Space Policy and Strategy. The African Union (AU) has been instrumental in promoting a coordinated approach to space activities on the continent. The African Space Policy and Strategy, adopted in 2016, aims to strengthen regional cooperation and build a sustainable space industry in Africa.
Collaborations with Global Space Agencies. African nations are increasingly collaborating with global space agencies such as NASA, ESA, and the Chinese National Space Administration (CNSA). These partnerships facilitate technology transfer, capacity building, and joint missions, enhancing Africa’s space capabilities.
Public-Private Partnerships. Public-private partnerships are playing a vital role in advancing Africa’s space industry. Companies like SpaceX and OneWeb are working with African governments and organizations to improve satellite communication and expand internet access across the continent.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Building Technical Expertise. One of the significant challenges facing Africa’s space industry is the need for skilled professionals and technical expertise. Investing in education and training programs is crucial for building a workforce capable of sustaining and advancing space initiatives.
Infrastructure Development. Developing the necessary infrastructure for space activities, such as launch facilities and ground stations, is essential for the growth of Africa’s space industry. Continued investment in infrastructure will enable more countries to participate in and benefit from space exploration.
Sustainable Funding. Securing sustainable funding is a critical challenge for space programs in Africa. Governments, international organizations, and private investors must work together to provide the financial resources needed to support ongoing and future space projects.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship. Encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship in the space sector can drive growth and create new opportunities. Supporting startups and fostering a culture of innovation will help Africa develop homegrown solutions and technologies for space exploration.
Conclusion
The last five years have witnessed remarkable developments in Africa’s space industry, marked by significant satellite launches, the rise of national space agencies, and increased international collaboration. These advancements have not only enhanced technological capabilities but also contributed to socio-economic development and environmental sustainability across the continent. As Africa continues to invest in space technology and build on these achievements, the future looks promising for the continent’s space industry.
FAQs
What are some of the recent satellite launches in Africa? Recent satellite launches in Africa include Ethiopia’s ETRSS-1, Egypt’s TIBA-1, South Africa’s ZACube-2, Nigeria’s Sat-2 and Sat-X, and Ghana’s GhanaSat-1.
How is satellite technology improving connectivity in Africa? Satellite technology is improving connectivity in Africa by providing high-speed internet and reliable communication services to remote and underserved regions, facilitating education, healthcare, and economic activities.
What role do international collaborations play in Africa’s space industry? International collaborations with global space agencies and organizations facilitate technology transfer, capacity building, and joint missions, enhancing Africa’s space capabilities and fostering regional cooperation.
What are the main challenges facing Africa’s space industry? The main challenges facing Africa’s space industry include building technical expertise, developing infrastructure, securing sustainable funding, and encouraging innovation and entrepreneurship.
How is space technology supporting agricultural development in Africa? Space technology supports agricultural development in Africa by providing critical information on soil health, crop conditions, and weather forecasts through satellite imagery and remote sensing, leading to better crop management and increased productivity.
What is the African Space Policy and Strategy? The African Space Policy and Strategy, adopted by the African Union in 2016, aims to promote regional cooperation, build a sustainable space industry, and enhance the socio-economic benefits of space activities across the continent.



